
Menu

Is the sea buckthorn berry truly deserving of its antioxidant-rich status? To answer this question, it’s crucial to understand the intricate interplay between antioxidants, free radicals, and oxidative damage.
Antioxidants play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help protect cells from damage, reduce inflammation, and support the body’s natural defence systems. Studies suggest that a diet rich in antioxidants may lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that contain unpaired electrons. They are produced naturally during metabolism, but their levels can increase due to factors such as exposure to pollution, UV radiation, and unhealthy lifestyle choices like smoking and poor diet. Excessive free radicals can lead to oxidative stress, triggering a cascade of cellular damage and contributing to various health problems.
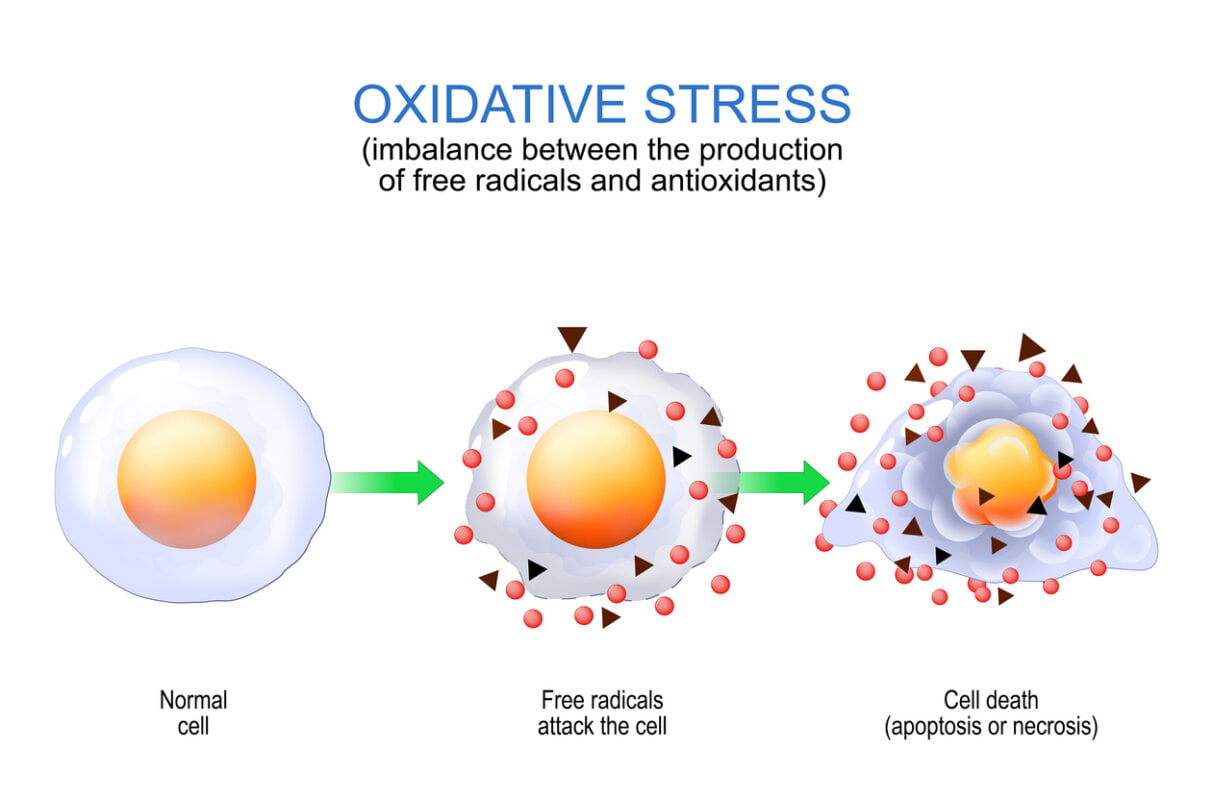
Oxidative stress occurs when there’s an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them with antioxidants. This imbalance can lead to cellular damage and is associated with various health issues. Signs of oxidative stress in humans may include:
Long-term oxidative stress is like constantly attacking your body’s cells. It can lead to problems like chronic inflammation, damage to your DNA, and an increased risk of diseases like heart problems, memory loss, and even cancer. It’s like your body is aging faster than it should, making you more vulnerable to getting sick and feeling tired all the time. Eating foods rich in antioxidants and practicing self-care is important to fight off this ongoing stress on your body.
While the body naturally produces antioxidants, they can also be obtained from food sources. Common antioxidants include vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and various minerals and phytochemicals found in fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based foods.
Vitamin C: Vitamin C is crucial in scavenging free radicals, regenerating vitamin E, supporting collagen synthesis, and enhancing immune function.
Vitamin E: Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant found in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils. It protects cell membranes from oxidative damage, helps maintain cardiovascular health, and supports skin integrity.
Carotenoids, including beta-carotene and lycopene: Beta-carotene is a precursor to vitamin A found in orange, yellow, and dark green fruits and vegetables, while lycopene is associated with reducing the risk of certain cancers and protecting against UV damage to the skin. These powerful antioxidant carotenoids are particularly beneficial for eye health, immune function, and skin health.
Selenium: Selenium is a component of selenoproteins, which have antioxidant properties and play roles in thyroid function, immune response, and DNA repair.
Zinc: While zinc itself may not directly scavenge free radicals like some other antioxidants, its involvement in enzyme function, glutathione metabolism, and metal ion regulation contributes to overall antioxidant defence and cellular protection against oxidative stress. Therefore, ensuring adequate zinc intake through diet is essential for maintaining optimal antioxidant status and overall health.
Phenolic compounds: Exhibit antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and cancer prevention.

Phenolic compounds are a diverse group of organic compounds found abundantly in plants. They are characterized by having one or more hydroxyl groups attached to an aromatic ring. Phenolic compounds serve various functions in plants, including protection against pathogens, UV radiation, and oxidative stress. In human nutrition, they are valued for their antioxidant properties and potential health benefits.
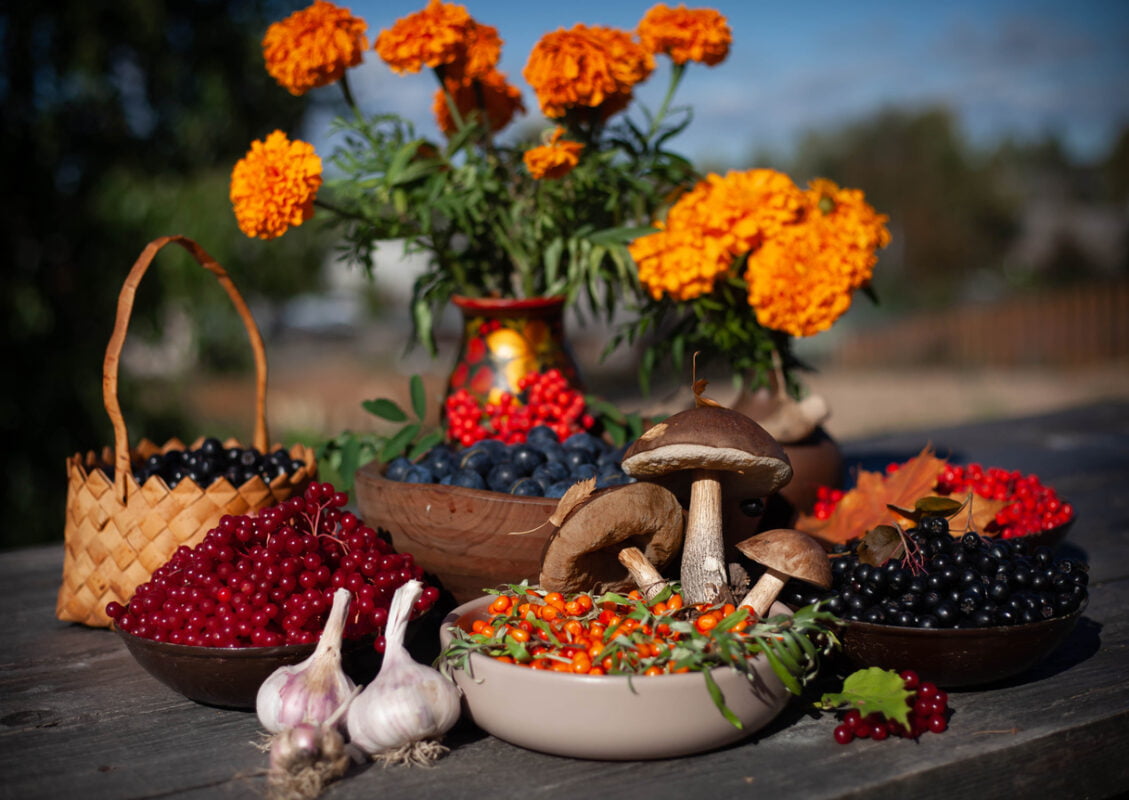

To answer the question the title of this article poses; Considering the detrimental effects of long-term oxidative stress on health, Sea buckthorn emerges as a potent ally in the battle against free radicals, offering a rich source of antioxidants to bolster the body’s defence mechanisms. Packed with an array of essential antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, selenium, zinc, beta-carotenes, and phenolic compounds, sea buckthorn berries provide powerful protection against oxidative damage. Including sea buckthorn in your diet can help neutralize free radicals, reduce inflammation, and promote overall well-being. Whether consumed fresh, as a juice or incorporated into recipes, sea buckthorn offers a natural and effective strategy for enhancing antioxidant intake and safeguarding against the long-term effects of oxidative stress.
The short answer is; yes, sea buckthorn is a food rich in antioxidants!
BENEFITS
With 70% of our immune system residing in our gut, what we put into it, counts! Sea buckthorn juice is known to help achieve balanced nutrient intake, cold and flu resistance and increased energy levels. It’s inflammation reducing antioxidants help athletes fight body fatigue, and the balanced Omegas fatty acids 3 – 6, 7* & 9, are considered to have a clear role in the prevention and healing of certain Atopic disorders.
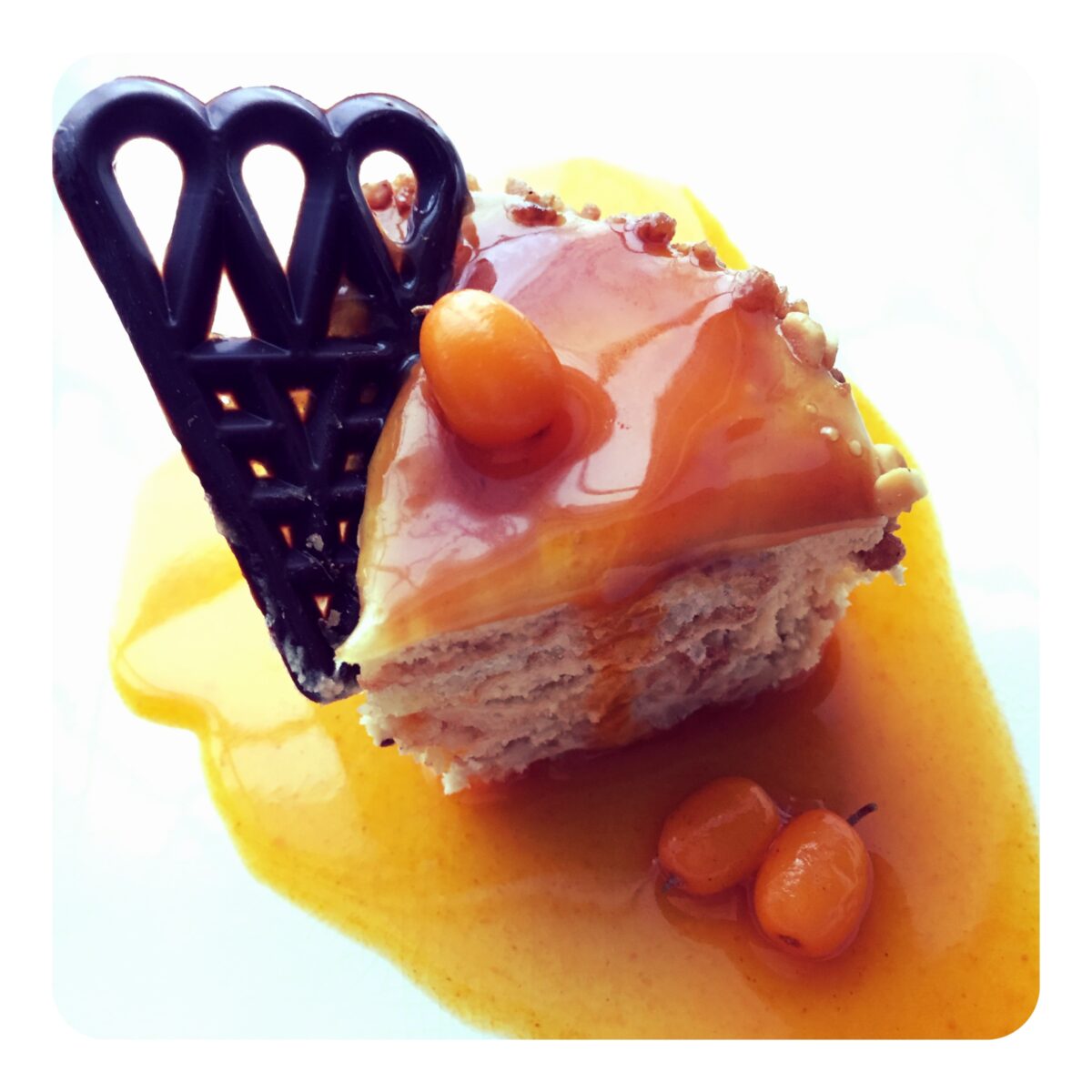

Sea buckthorn coulis
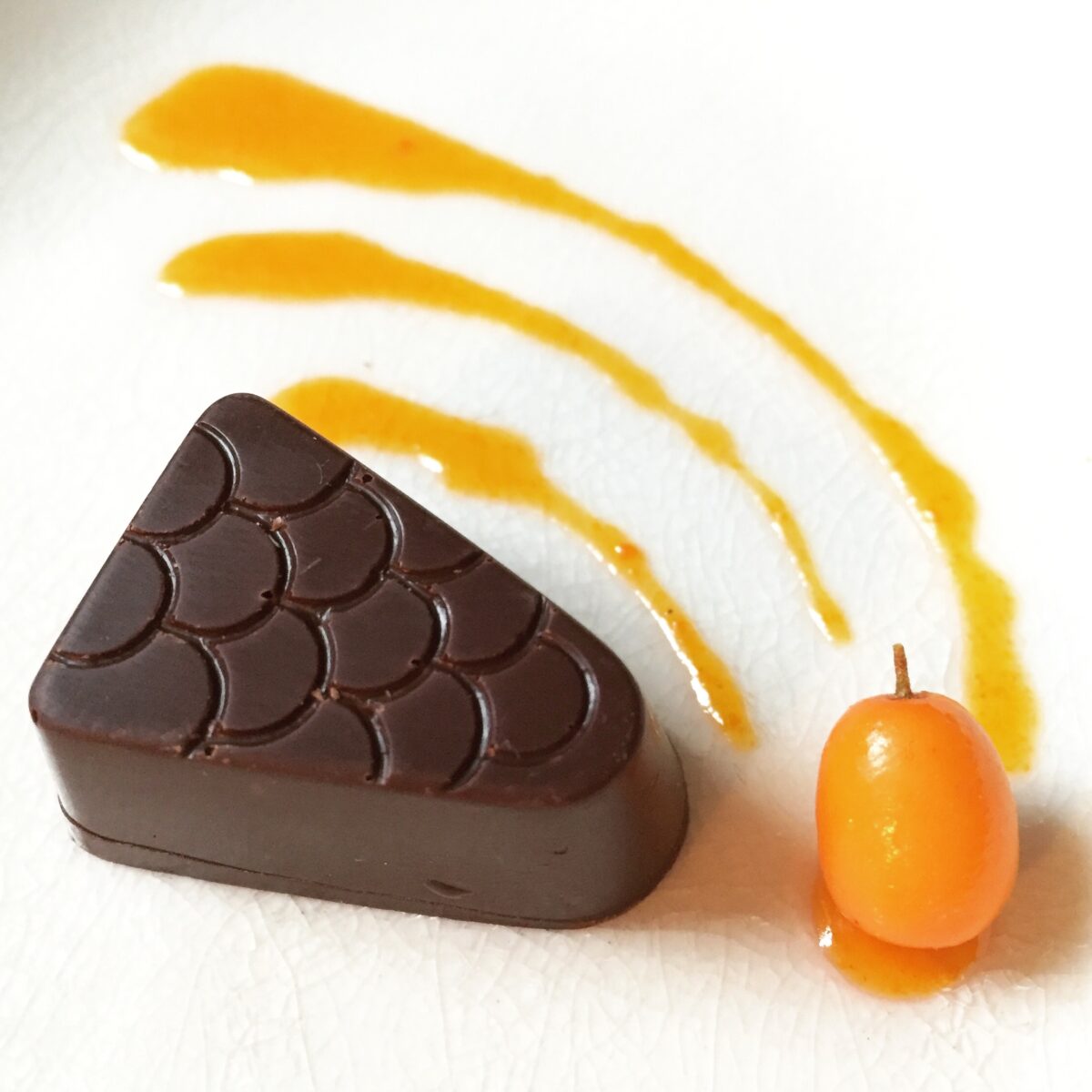

Delicious Sea buckthorn ganache inside dark chocolat shell.
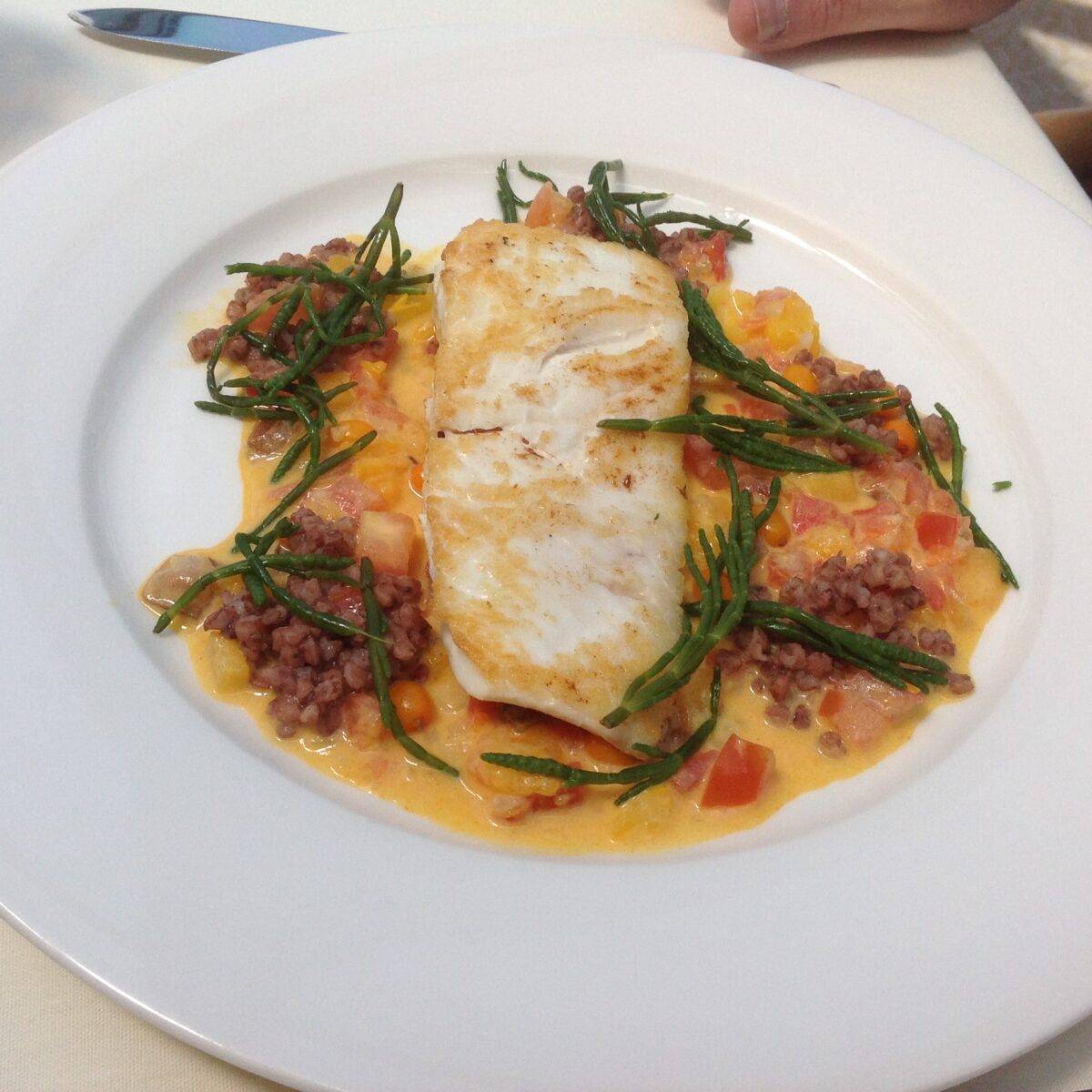

Halibut with sea buckthorn, tomato and sea beans.
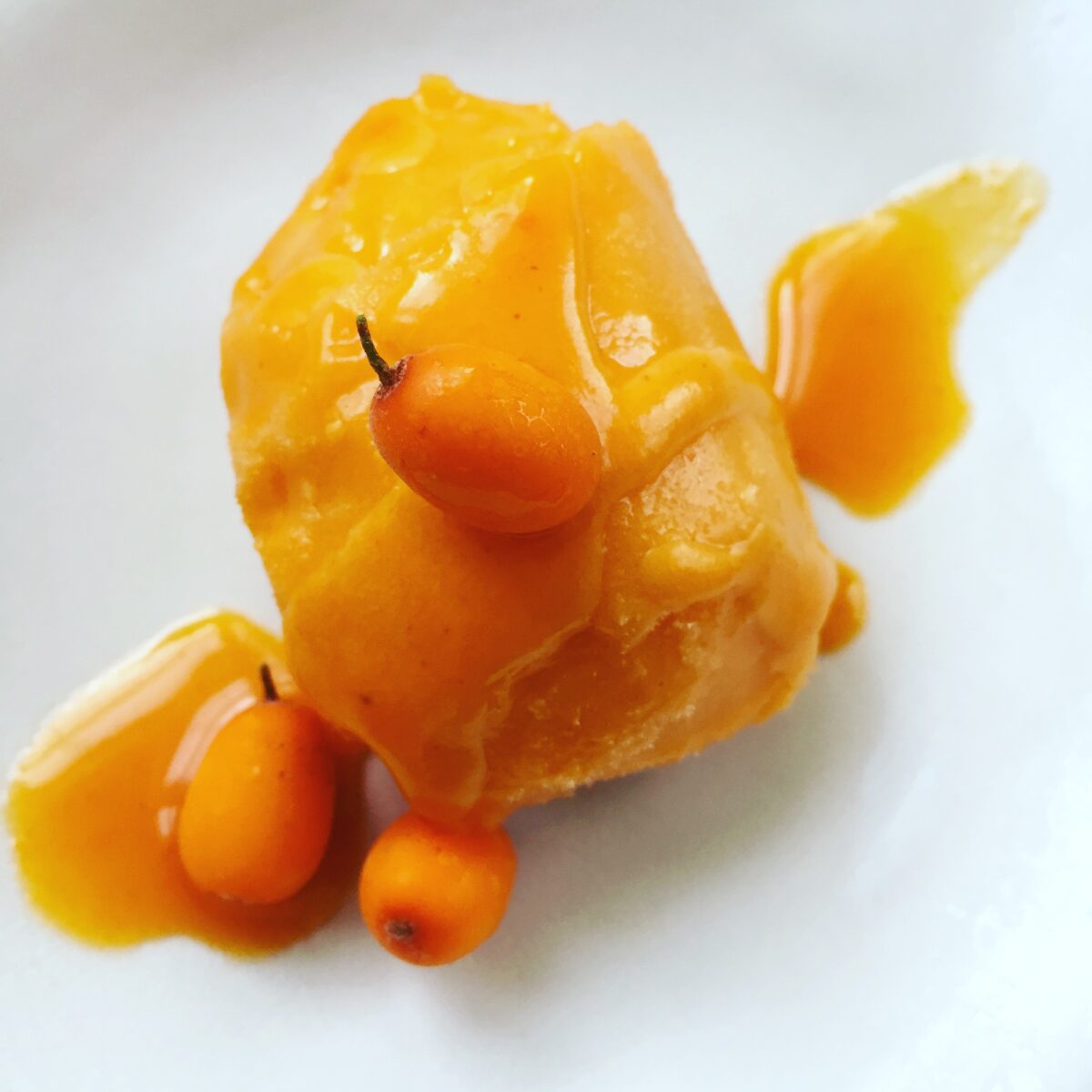

Homemade Seaberry sorbet.
 Frozen Sea Buckthorn berries (IQF)
Frozen Sea Buckthorn berries (IQF)
 Sea Buckthorn Shrubs | cultivar: LORD
Sea Buckthorn Shrubs | cultivar: LORD


A Brief History of Kombucha Centuries before we could identify probiotic microbes with microscopes, people were fermenting

Add a healthy punch to your summer cocktails Summer is perfect for patio chit-chats with close

Should Sea Buckthorn be considered a natural supplement? In the vast landscape of natural supplements, Sea